Laboratory testing
High temperature aging in non-aggressive fluids
This is the second in a series of articles discussing long-term durability testing of well sealants. This article discusses the importance of aging conditions (surrounding media and temperature profile) and suggests a possibility for accelerated aging of Portland cement/silica systems.
Read more
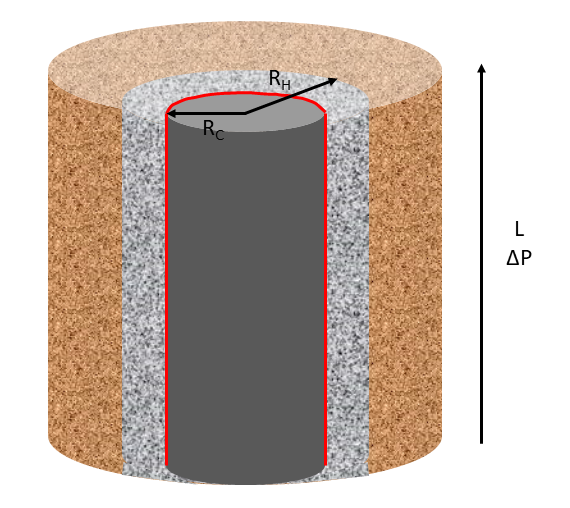
Long-term durability testing - effect of sample geometry
This is the first in a series of articles discussing long-term durability testing of well sealants. This article discussions the importance of sample geometry in laboratory testing in comparison with different well situations.
Read more
The membrane test - key experimental parameters
The membrane test is used to determine the bulk volume changes of cement systems under impermeable conditions. To ensure that the results are representative particular attention must be paid to several key experimental parameters.
Read more
Compressive strength measurements – the effect of slurry stability
Compressive strength measurements on cement systems only provide useful results for slurries that are stable, i.e. slurries that have little or no sedimentation or free fluid generation. Read more
Compressive strength measurements at high temperature
The reasons behind the reduction in compressive strength that is sometimes observed during compressive strength determination (cube tests and UCA measurements) at temperatures above 110°C even when the system contains at least 35% bwoc silica. Read more
Rheological measurements
A discussion of some errors in rheological measurements of cement slurries seen in published documents and comparisons of model fits (Bingham and Herschel-Bulkley) to the data. Read more
Sedimentation tests
A discussion of some experimental observations from sedimentation tests (API RP10B-2) at high temperatures. Read more
Cement chemistry
Portland cement chemistry and hydration reactions
The first in a series of articles covers cement chemical notation, Portland cement components and their hydration reactions. Read more
Chemical shrinkage of hydraulic binders
The second in a series of articles gives an explanation of chemical shrinkage, with two examples, and a method of measuring chemical shrinkage of hydraulic binders. Read more
Bulk volume changes of Portland cement systems
The third article in the series discusses how the effect of chemical shrinkage on the bulk volume changes will depend significantly on the conditions during setting, and considerations for oil well cementing. Read more

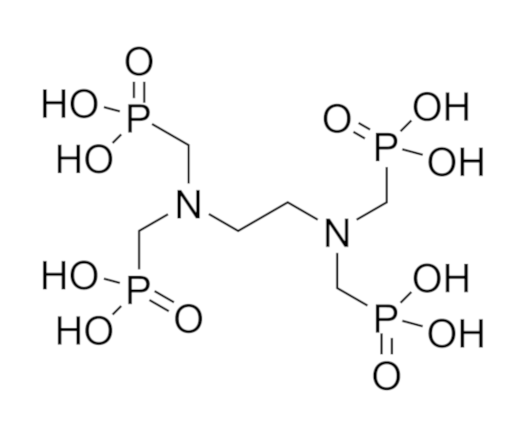
Additives
Anti-settling agents
The two most common biopolymer anti-settling agents are Welan and Diutan gums. Read more
Latex additives for gas migration control
Latex additives for gas migration control, with a list of suppliers. Read more
Expanding agents
This article explains how expanding agents can be used to reduce the risk of loss of zonal isolation in both annular and plug configurations. Read more